COVID 19 may affect Central Nervous System causing loss of smell & taste: Study
Sun 26 Apr 2020, 22:24:44
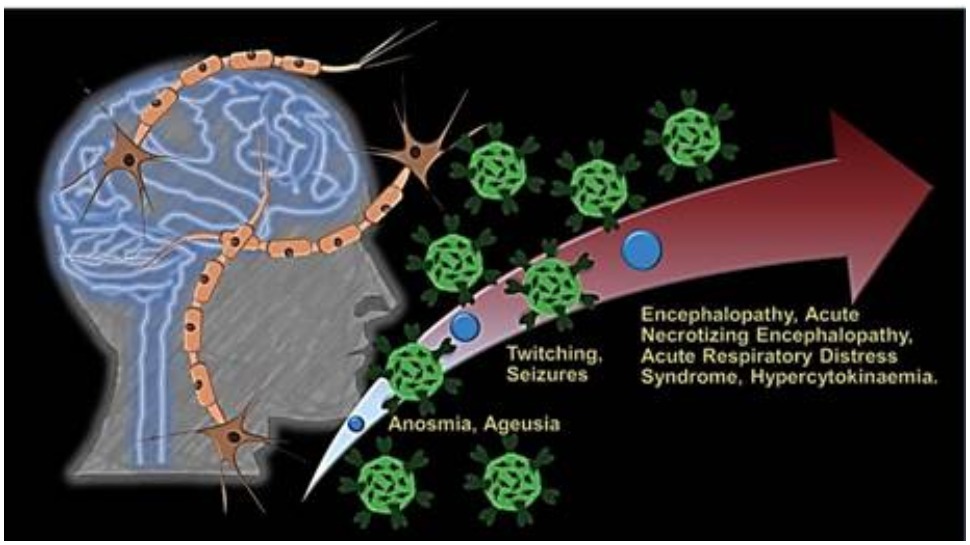
New Delhi: While exploring the neuroinvasive nature of the COVID 19 virus SARS-CoV-2, the Jodhpur Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) has highlighted that this can affect the Central Nervous System causing loss of smell and taste of infected patients.
Dr. Surajit Ghosh and his team at IIT Jodhpur have
pointed out that SARS-CoV-2 is known to interact with a specific human receptor known as hACE2 (human angiotensin-converting enzyme-2) which also happens to be the entry point of the virus and has an almost ubiquitous presence in most human organs ranging from lung parenchyma to nasal mucosa. The brain is also known to express this receptor.
pointed out that SARS-CoV-2 is known to interact with a specific human receptor known as hACE2 (human angiotensin-converting enzyme-2) which also happens to be the entry point of the virus and has an almost ubiquitous presence in most human organs ranging from lung parenchyma to nasal mucosa. The brain is also known to express this receptor.
No Comments For This Post, Be first to write a Comment.
Most viewed from Coronavirus Updates
Most viewed from Health
AIMIM News
Latest Urdu News
Most Viewed
May 26, 2020
Can Lionel Messi's visit boost Indian football?
Latest Videos View All
Like Us
Home
About Us
Advertise With Us
All Polls
Epaper Archives
Privacy Policy
Contact Us
Download Etemaad App
© 2025 Etemaad Daily News, All Rights Reserved.





























.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)


