How olive oil could prevent heart attacks and strokes
Fri 07 Sep 2018, 16:12:41
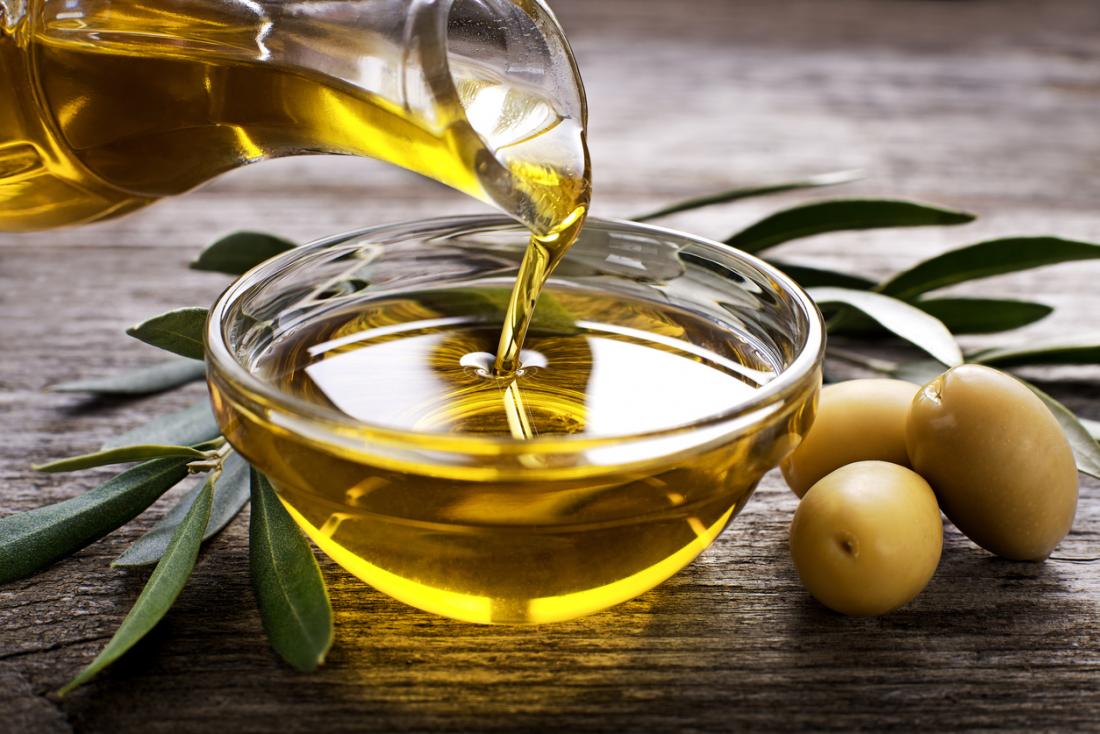

Turns out, food high in unsaturated fat may protect against cardiovascular diseases.
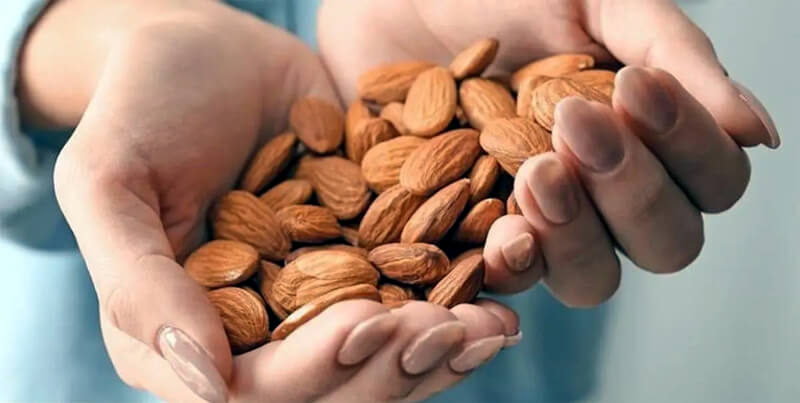
Levels of ApoA-IV increase after the digestion of foods, particularly foods high in unsaturated fats, such as olive oil. Higher levels of ApoA-IV in the blood have been reported to be associated with lower rates of cardiovascular disease.
Apolipoprotein A-IV, known as ApoA-IV, is a plasma protein.
New research from the Keenan Research Centre for Biomedical Science (KRCBS) of St. Michael's Hospital demonstrates that ApoA-IV is an inhibitory factor for platelets, which are small blood cells that play a key role in multiple diseases, particularly in bleeding and cardiovascular diseases.
These new findings suggest that ApoA-IV is a blocker of platelet surface glycoproteins GPIIbIIIa. Platelet aggregation can cause vessel occlusion that blocks blood flow, leading to thrombosis, which is the most common cause of mortality and morbidity worldwide.
Principal investigator of the study Dr. Heyu Ni said, "Platelet aggregation can save lives because it can stop bleeding in damaged vessels. But we usually don't want platelets to block blood flow in the vessels. This is thrombosis, and if vessel occlusion
occurs in the heart or brain, it can cause heart attack, stroke or death."
occurs in the heart or brain, it can cause heart attack, stroke or death."
The researchers also examined ApoA-IV's interaction with food. After every meal, platelets are stimulated, which makes it easier for them to bond together or bond to white blood cells. ApoA-IV increases in circulating blood almost immediately after meals containing unsaturated fats and decreases platelet hyperactivity and bonding, thus reducing the inflammation after meals and the risk of heart attack and stroke.
The study also found that ApoA-IV has its own circadian rhythm. It is most active overnight and least active in the morning.
"Mother Nature wants us to sleep well," said Dr. Ni. "So we are protected by this protein while we sleep, and most likely to experience a cardiovascular event after waking up in the morning."
Dr. Ni and his team are excited about these findings because they show that foods with high unsaturated fats, along with appropriate sleep patterns, create the perfect combination for the protein ApoA-IV to play a positive role in reducing the chances of cardiovascular disease in the form of atherosclerosis, heart attack, or stroke.
The full findings are present in the journal- Nature Communications.
No Comments For This Post, Be first to write a Comment.
Most viewed from Health
AIMIM News
Latest Urdu News
Most Viewed
May 26, 2020
Do you think Canada-India relations will improve under New PM Mark Carney?
Latest Videos View All
Like Us
Home
About Us
Advertise With Us
All Polls
Epaper Archives
Privacy Policy
Contact Us
Download Etemaad App
© 2025 Etemaad Daily News, All Rights Reserved.