Know signs and symptoms to detect leukemia at an early age in children
Thu 02 Nov 2023, 00:30:45
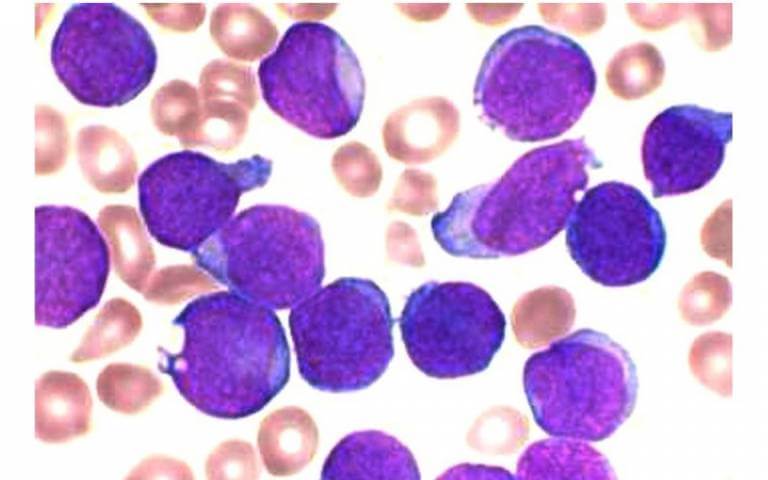
Leukemia accounts for approximately 30% of all childhood cancers in India, making it the most common form of pediatric cancer. Affecting thousands of families across the country, Leukemia is a cancer of the blood and bone marrow. It emerges when the body's white blood cells, responsible for fighting infections, undergo abnormal growth and reproduction. This abnormal proliferation leads to an overproduction of immature white blood cells, which can crowd out healthy blood cells and impair the body's ability to fight infections and transport oxygen.
There are two main types of childhood leukaemia: acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) and acute myeloid leukaemia (AML). ALL is the most common type, accounting for approximately 75% of cases. The precise causes of childhood leukemia remain the subject of ongoing research. Experts believe that some genetic mutations might increase susceptibility to leukemia, and environmental factors like radiation and chemical exposures could contribute to certain cases.
Identifying the signs and symptoms of leukemia in children is critical for early detection. While advancements in medical technology have improved diagnosis and treatment options, the problem of delayed diagnosis persists. Many children are still diagnosed at advanced stages, reducing the likelihood of successful treatment. Hence, the early identification of symptoms holds the key to effectively combating this life-threatening disease. These symptoms may be subtle and mimic common childhood illnesses, including:
. Unusual tiredness and weakness.
. A weakened immune system leads to frequent infections.
. Unexplained and persistent fevers.
. Easy
bruising or prolonged bleeding.
bruising or prolonged bleeding.
. Complaints of pain in bones or joints.
. Swollen lymph nodes, abdomen, or liver.
. Significant decrease in appetite and unexplained weight loss.
While these symptoms can be indicative of various childhood ailments, it's crucial not to overlook persistent, unexplained symptoms. If any of these signs persist for an extended period, consulting a healthcare professional is essential. Childhood leukemia is a complex and challenging condition that demands a multidisciplinary approach involving oncologists, haematologists, and other medical professionals, along with the unwavering support of families and caregivers.
If leukemia is suspected in a child, a series of tests, including blood tests and bone marrow aspiration, may be conducted for confirmation. Once diagnosed, treatment options may include:
Chemotherapy: Utilizing a combination of drugs to target and kill cancer cells.
Radiation Therapy: High-energy rays directed at cancer cells for destruction.
Stem Cell Transplant: Replacement of damaged or destroyed bone marrow with healthy stem cells.
Targeted Therapy: Medications that specifically target cancer cells.
Immunotherapy: Boosting the immune system to fight leukaemia cells.
Treatment choices depend on the type and stage of leukemia and the child's overall health. Understanding the risk factors associated with childhood leukemia and seeking medical attention promptly when symptoms arise can make a significant difference in a child's prognosis. Additionally, medical advancements offer hope for successful treatment and long-term recovery.
No Comments For This Post, Be first to write a Comment.
Most viewed from Health
AIMIM News
Latest Urdu News
Most Viewed
May 26, 2020
Do you think Canada-India relations will improve under New PM Mark Carney?
Latest Videos View All
Like Us
Home
About Us
Advertise With Us
All Polls
Epaper Archives
Privacy Policy
Contact Us
Download Etemaad App
© 2025 Etemaad Daily News, All Rights Reserved.