Know the causes and risk factors of premature birth
Fri 28 Jun 2024, 00:08:17
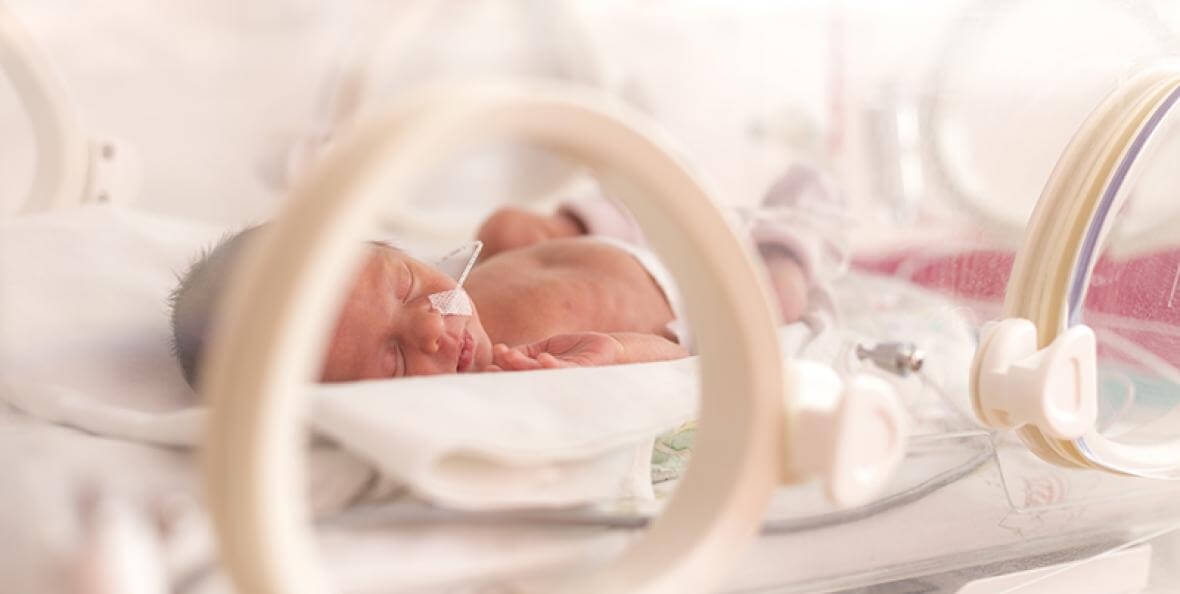

Premature delivery, a global public health concern, is often known as low birth weight, which means the birth of a child before the 37-week gestational period. Each year, over one million babies are born prematurely, making up 10% of all births. This condition results in numerous health complications and poses a considerable psychological burden on families. To effectively prevent and manage cases of premature birth, it is imperative to understand the causes and risk factors of this condition.
Causes of Premature Birth
When we spoke to Dr Aparna Jha, MBBS, MS, DNB, MRCOG, Apollo Cradle & Children’s Hospital, Marathahalli, Bangalore, regarding the same, she said that premature birth is often the result of a complex interplay of various factors, including medical conditions, lifestyle choices, and environmental influences. Some of the primary causes include:
Medical Conditions
Certain medical conditions in the mother can significantly increase the risk of premature birth.
These include:
Chronic Health Issues: Pre-existing diseases such as diabetes, high blood pressure, and hormonal disorders like thyroid may lead to complications that make labour commence early.
Multiple Pregnancies: People expecting twins, triplets, and multiple pregnancies face higher risks of premature labour since the body of the woman is subjected to extra strain.
Cervical Insufficiency: Cervical insufficiencies may also make the cervix dilate and cause labour when it is not supposed to happen.
Placental Problems: Placental abruption or placenta previa which are complications that become apparent after 20 weeks of pregnancy might require abdominal delivery at the time of birth, for both
mother and baby to be healthy.
mother and baby to be healthy.
Lifestyle Factors
Lifestyle choices and behaviours also play a significant role in the risk of premature birth. These factors include:
Smoking and Substance Use: Tobacco, alcohol, and illicit drug use during pregnancy are strongly linked to premature birth.
Poor Nutrition: Inadequate maternal nutrition can lead to fetal growth restriction and increase the likelihood of preterm labour.
High-Stress Levels: Chronic stress can affect hormonal balances and immune responses, contributing to preterm birth.
Environmental Exposures: Harmful substances, which are found in the environment in the form of pollutants or chemicals can also impact pregnancy.
Some significant risk factors include:
Previous Premature Birth
Pregnant women who previously gave birth to a premature baby are more likely to record another case.
Age of the Mother
Teenage mothers or mothers who give birth before the age of 18 years have higher premature birth risks than those mothers who are above 35 years of age. In teenage pregnancies, some of the challenges include low levels of prenatal care and poor standards of nutrition. Additionally, some pregnant women are also victims of chronic diseases.
Reproductive Technology
New technologies like IVF lead to multiple pregnancies, which increases the chances of early deliveries as well.
Short Interpregnancy Interval
Gestational cycling meaning close childbearing succession, in less than six months, may lead to preterm labour because the mother has not fully recovered.
No Comments For This Post, Be first to write a Comment.
Most viewed from Health
AIMIM News
Latest Urdu News
Most Viewed
May 26, 2020
Do you think Canada-India relations will improve under New PM Mark Carney?
Latest Videos View All
Like Us
Home
About Us
Advertise With Us
All Polls
Epaper Archives
Privacy Policy
Contact Us
Download Etemaad App
© 2025 Etemaad Daily News, All Rights Reserved.