Vitamin D supplements linked with lower diabetes risk: Study
Wed 08 Feb 2023, 13:05:15

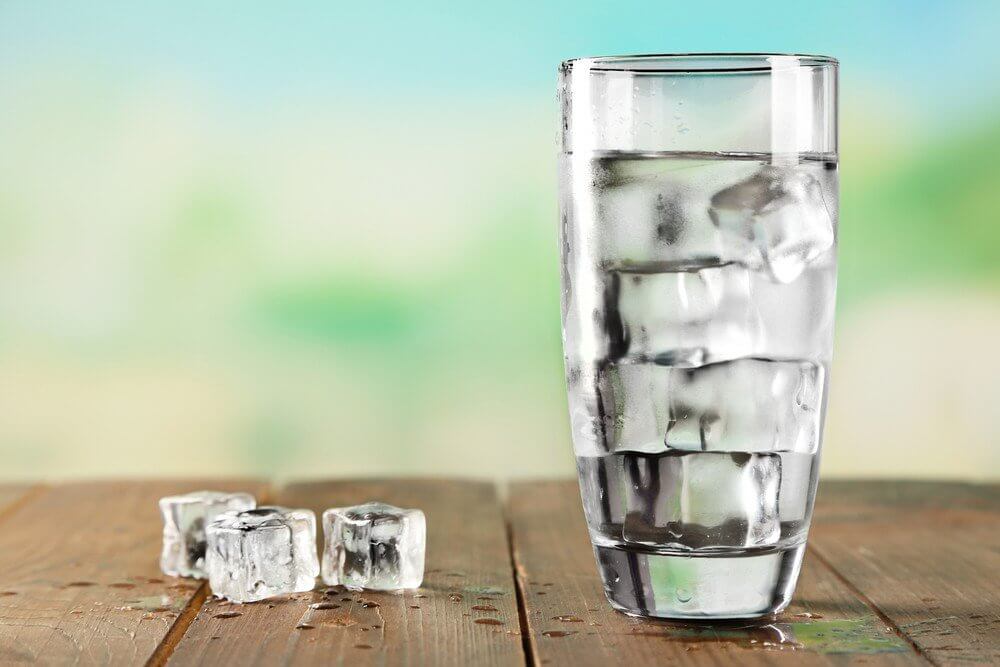
Boston: Higher vitamin D intake may be associated with a lower risk of developing type 2 diabetes in adults with prediabetes, a review of clinical trials has found.
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin available in or added to some foods, as
a supplement, or produced by the body when ultraviolet rays from sunlight strike the skin.
a supplement, or produced by the body when ultraviolet rays from sunlight strike the skin.
Vitamin D has many functions in the body, including a role in insulin secretion and glucose metabolism.
No Comments For This Post, Be first to write a Comment.
Most viewed from Health
AIMIM News
Latest Urdu News
Most Viewed
May 26, 2020
Do you think Canada-India relations will improve under New PM Mark Carney?
Latest Videos View All
Like Us
Home
About Us
Advertise With Us
All Polls
Epaper Archives
Privacy Policy
Contact Us
Download Etemaad App
© 2025 Etemaad Daily News, All Rights Reserved.