Hyderabad-based NGRI develops India’s first earthquake strain map
Sun 06 Apr 2025, 22:42:46
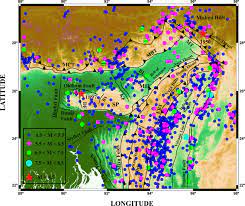
The seismologists of Hyderabad-based National Geophysical Research Institute (NGRI) have developed India’s first strain map to assess earthquake vulnerability in the Himalayan and Indo-Gangetic regions.
Director, NGRI, Prakash Kumar, while interacting with Dr Jitendra Singh, Union Minister of State (Independent Charge) for Science & Technology on Sunday, said that the strain map to assess earthquake vulnerability is a critical step towards disaster preparedness.
Strain map, essentially utilises the geodetic data culled from instruments like GPS to measure the movements and deformations of the surface. Such measurements capture the strain that accumulates in the Earth’s crust due to tectonic forces.
The NGRI strain map could be useful to pinpoint regions in Himalayas that are prone to earthquakes in the future. The strain maps can also be applied to assess the risks that a particular regions faces, in addition to relying on historical earthquake data. Such tools, essentially, enable the local State governments towards disaster preparedness.
“We are also conducting deep seismic profiling under a national programme aimed at decoding the crustal structure of central India, which holds implications for both tectonic studies and mineral exploration. Our work on geothermal energy, particularly in Ladakh and Chhattisgarh, has opened new frontiers for clean and renewable energy,” NGRI Director
said.
said.
The three Directors of Hyderabad-based CSIR laboratories including NGRI, Centre for Cellular and Molecular Biology (CCMB) and Indian Institute of Chemical Technology (IICT) presented their institute’s achievements, during a review the Union Minister for Science and Technology.
Speaking on the occasion, Director, IICT, Dr D Srinivasa Reddy said that the chemical research institute’s researchers developed safer and more effective agrochemicals, and its work in catalysis has led to novel catalysts for hydrogenation, oxidation, and polymerization processes used widely in industrial applications.
“IICT has developed compostable plastics in association with GreenWorksBio. We have also developed Hydrazine Hydrate in collaboration with Gujarat Alkalies and Chemicals Limited (GACL),” he said.
Director, CCMB, Dr Vinay Nandicoori highlighted the recent success it has achieved through sickle cell anemia diagnostics. “One of CCMB’s most impactful initiatives has been its work on sickle cell anemia, under which it developed a highly sensitive, low-cost diagnostic kit as part of the National Sickle Cell Elimination Mission,” he said.
On the occasion, Dr Jitendra Singh appreciated the vital role played by the three CSIR laboratories in driving scientific innovation, supporting national missions, and contributing to India’s goal of becoming a self-reliant knowledge economy.
No Comments For This Post, Be first to write a Comment.
Most viewed from Hyderabad
Most viewed from World
AIMIM News
Latest Urdu News
Most Viewed
May 26, 2020
Which Cricket team will win the IPL 2025 trophy?
Latest Videos View All
Like Us
Home
About Us
Advertise With Us
All Polls
Epaper Archives
Privacy Policy
Contact Us
Download Etemaad App
© 2025 Etemaad Daily News, All Rights Reserved.






.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)































