Nasa has announced two missions to Venus by 2030
Tue 08 Jun 2021, 09:41:54
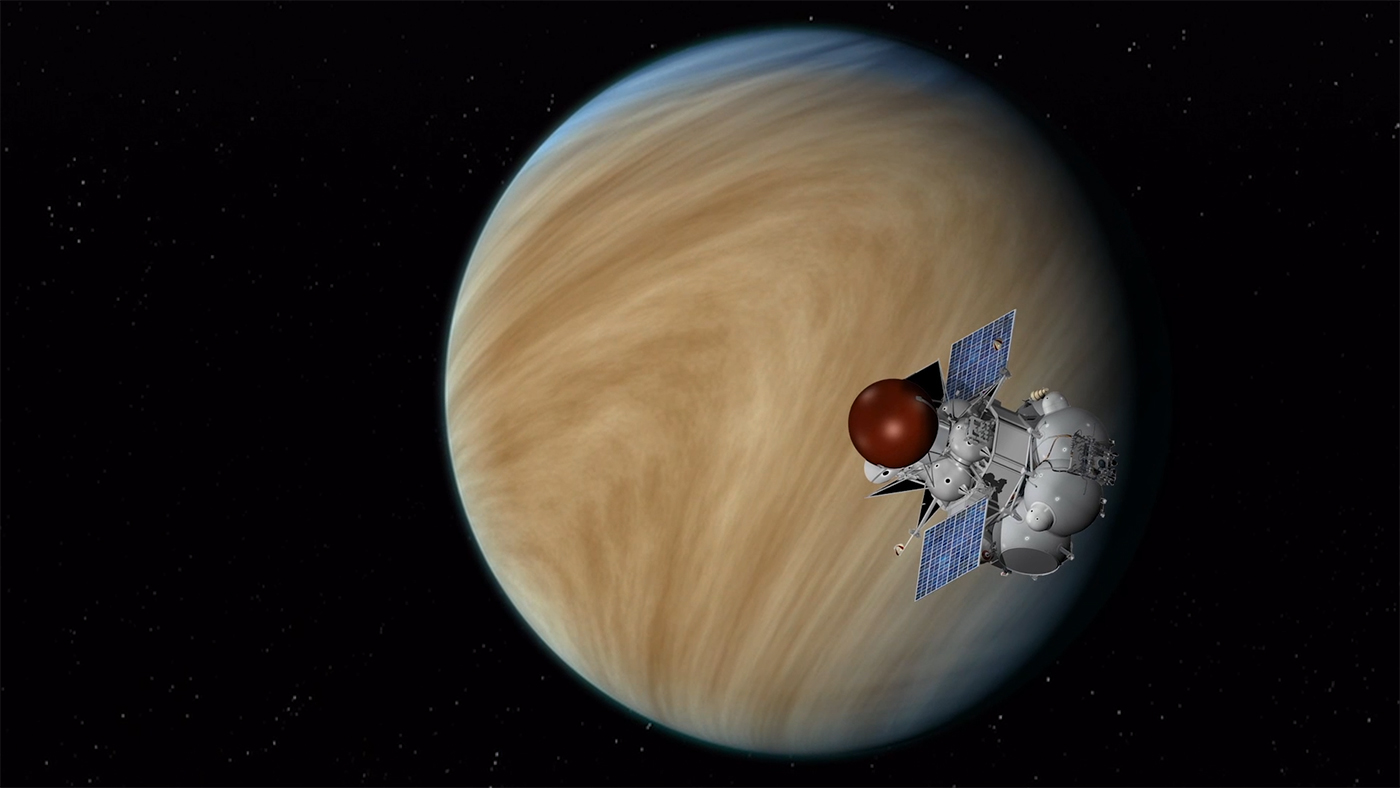
Nottingham (UK):For decades, the exploration of our solar system left one of our neighbouring planets, Venus, largely unexplored. Now, things are about to change.
In the latest announcement from Nasa's solar system exploration programme, two missions have been given the go-ahead – and they're both bound for Venus. The two ambitious missions will launch between 2028 and 2030.
This marks a considerable change in direction for Nasa's planetary science division, which hasn't sent a mission to the planet since 1990. It's exciting news for space scientists like me.
Venus is a hostile world. Its atmosphere contains sulphuric acid and the surface temperatures is hot enough to melt lead. But it has not always been this way. It is thought Venus started out very similar to the Earth. So what happened?
While on Earth, carbon is mainly trapped in rocks, on Venus it has escaped into the atmosphere – making it roughly 96 per cent carbon dioxide. This has led to a runaway greenhouse effect, pushing surface temperatures up to 750 kelvin (470 degree celsius or 900 degree Fahrenheit).
The planet's history makes it an excellent place to study the greenhouse effect and to learn how to manage it on Earth. We can use models which plot the atmospheric extremes of Venus, and compare the results to what we see back home.
But, the extreme surface conditions are one of the reasons planetary exploration missions have avoided Venus. The high temperature means a very high pressure of 90 bars (equivalent to roughly one kilometre underwater) which is enough to instantly crush most planetary landers. It might not come as a surprise, then, that missions to Venus haven't always gone to plan.
Most of the exploration done so far was carried out by the then Soviet Union between the 1960s and the 1980s. There are some notable exceptions, such as Nasa's Pioneer Venus mission in 1972 and the
European Space Agency's Venus Express mission in 2006.
European Space Agency's Venus Express mission in 2006.
The first landing happened in 1970, when the Soviet Union's Venera 7 crashed due to the parachute melting. But it managed to transmit 20 minutes of data back to Earth. The first surface images were taken by Venera 9, followed by Veneras 10, 13 and 14.
The first of the two selected Nasa missions will be known as Davinci+ (a shortening of Deep Atmosphere of Venus Investigations of Noble Gases, Chemistry and Imaging). It includes a descent probe, meaning it will be dropped through the atmosphere, taking measurements as it goes. The descent has three stages with the first investigating the entire atmosphere.
The probe will be looking at the composition of the atmosphere in detail, providing information on each layer as it falls. We know sulphuric acid is confined to cloud layers at around 50km (30 miles) up, and we know that the atmosphere is 97 per cent carbon dioxide.
But studying trace elements can provide information on how the atmosphere ended up in this state. The second stage will be looking at lower altitudes to measure weather properties such as wind speed, temperature and pressure in detail.
The last stage take surface images in high resolution. While this is very common for Mars, it has always been a challenge on Venus. The thick cloud layer means visible light is reflected, so observing from Earth or from orbit isn't practical. The intense surface conditions also mean rovers are impractical. One suggestion has been a balloon mission.
We have a low resolution image of the surface of Venus, thanks to Nasa's Magellan mission in 1990, which mapped the surface using radar.
The Davinci probe will take surface images using infrared light during its descent. These pictures will not only allow better planning for future missions but also help scientists investigate how the surface formed.
No Comments For This Post, Be first to write a Comment.
Most viewed from International
Most viewed from World
AIMIM News
Latest Urdu News
Most Viewed
May 26, 2020
Do you think Canada-India relations will improve under New PM Mark Carney?
Latest Videos View All
Like Us
Home
About Us
Advertise With Us
All Polls
Epaper Archives
Privacy Policy
Contact Us
Download Etemaad App
© 2025 Etemaad Daily News, All Rights Reserved.





.jpg)
.jpg)


.jpg)































