ISRO's South Asian satellite GSLV-F09 blasts off from Sriharikota successfully
Fri 05 May 2017, 18:09:52
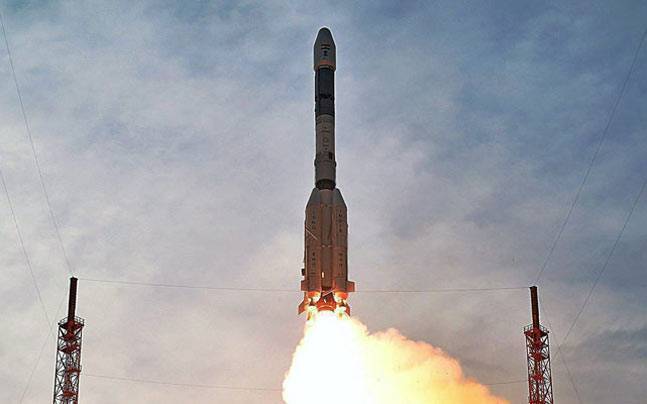

India's Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle-the South Asia Communication Satellite- was launched from the Second Launch Pad at Satish Dhawan Space Centre, Sriharikota, on Friday.
GSLV-F09 mission is the eleventh flight of GSLV and its fourth consecutive flight with the indigenous Cryogenic Upper Stage (CUS).
Seven of the eight SAARC countries--India, Sri Lanka, Bhutan, Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Nepal and Maldives, are a part of the project. Pakistan had decided to opt out, stating 'it has its own space programme.'
What is GSAT-9 ?
GSAT-9 is a
Geostationary Communication Satellite with the objective to provide various communication applications in Ku-band with coverage over South Asian countries.
Geostationary Communication Satellite with the objective to provide various communication applications in Ku-band with coverage over South Asian countries.
GSAT-9 is configured around the ISRO's standard I-2K bus, with lift off mass of 2230 kg.
The main structure of the satellite is cuboid in shape built around a central cylinder with a mission life of more than 12 years.
The satellite, costing around Rs 235 crore, is meant for providing communication and disaster support, connectivity among the countries of South Asia region. Its mission life will span 12 years.
No Comments For This Post, Be first to write a Comment.
Most viewed from National
Most viewed from World
AIMIM News
Delhi Assembly polls: Owaisi leads Padyatra in Okhla
Feb 01, 2025
We reject this Waqf Amendment Bill: Asaduddin Owaisi
Jan 30, 2025
Latest Urdu News
Most Viewed
May 26, 2020
Which political party will win the Delhi Assembly polls to be held on Feb 5?
Latest Videos View All
Like Us
Home
About Us
Advertise With Us
All Polls
Epaper Archives
Privacy Policy
Contact Us
Download Etemaad App
© 2025 Etemaad Daily News, All Rights Reserved.

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)





.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)