NASA's Juno spacecraft beams back first image of Jupiter
Wed 13 Jul 2016, 13:31:00
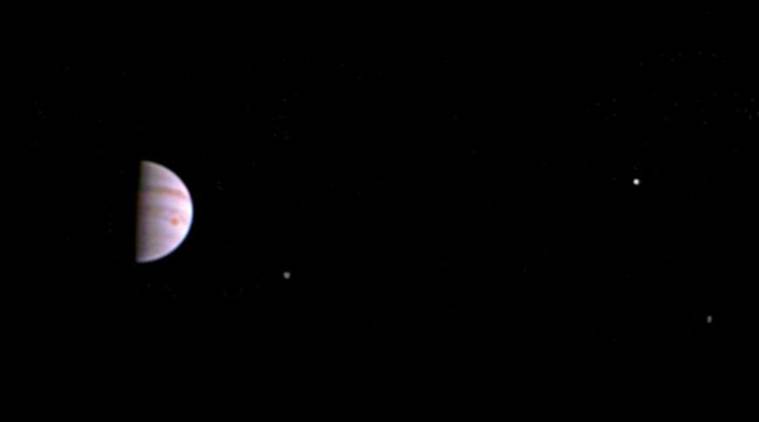

JunoCam - the camera aboard NASA's Juno mission - has sent back some of the first images of Jupiter along with three of its four largest moons taken after the spacecraft entered orbit around the king of planets on July 4.
Juno's visible-light camera was turned on six days after Juno fired its main engine and placed itself into orbit around the largest planetary inhabitant of our solar system. The first high-resolution images of the gas giant Jupiter are still a few weeks away.
"This scene from JunoCam indicates it survived its first pass through Jupiter's extreme radiation environment without any degradation and is ready to take on Jupiter," said Scott Bolton, from the Southwest Research Institute in San Antonio.
The new view was obtained when the spacecraft was 4.3 million kilometres from Jupiter on the outbound leg of its initial 53.5-day capture orbit. The colour image shows atmospheric features on Jupiter, including the famous Great Red Spot, and three of the massive planet's four largest moons - Io, Europa and Ganymede, from left to right in the image.
"JunoCam will continue to take images as we go around in this first orbit,"
said Candy Hansen, Juno co-investigator from the Planetary Science Institute in the US. "The first high-resolution images of the planet will be taken on August 27 when Juno makes its next close pass to Jupiter," Hansen said.
said Candy Hansen, Juno co-investigator from the Planetary Science Institute in the US. "The first high-resolution images of the planet will be taken on August 27 when Juno makes its next close pass to Jupiter," Hansen said.
JunoCam is a colour, visible-light camera designed to capture remarkable pictures of Jupiter's poles and cloud tops. As Juno's eyes, it will provide a wide view, helping to provide context for the spacecraft's other instruments.
JunoCam was included on the spacecraft specifically for purposes of public engagement; although its images will be helpful to the science team, it is not considered one of the mission's science instruments.
The Juno team is currently working to place all images taken by JunoCam on the mission's website, where the public can access them. During its mission of exploration, Juno will circle the Jovian world 37 times, soaring low over the planet's cloud tops - as close as about 4,100 kilometres.
During these flybys, Juno will probe beneath the obscuring cloud cover of Jupiter and study its auroras to learn more about the planet's origins, structure, atmosphere and magnetosphere.
No Comments For This Post, Be first to write a Comment.
Most viewed from Specials
Most viewed from World
AIMIM News
Latest Urdu News
Most Viewed
May 26, 2020
Do you think Canada-India relations will improve under New PM Mark Carney?
Latest Videos View All
Like Us
Home
About Us
Advertise With Us
All Polls
Epaper Archives
Privacy Policy
Contact Us
Download Etemaad App
© 2025 Etemaad Daily News, All Rights Reserved.